Tirzepatide – Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
Chemical Identity
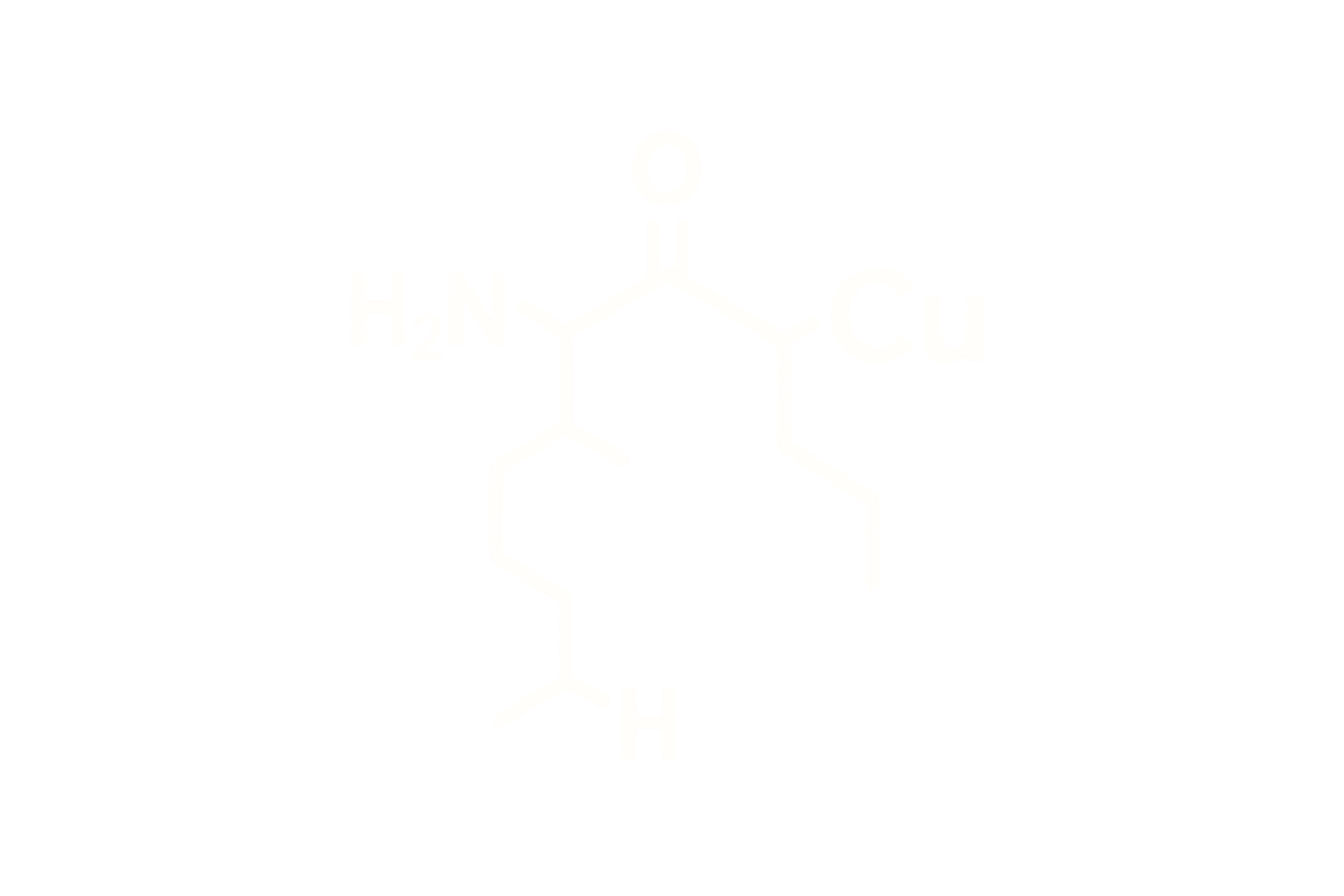
Chemical Name: Tirzepatide Acetate
Molecular Formula: C₂₂₇H₃₆₈N₄₈O₆₈
Molecular Weight: ~4813.5 Da
CAS Number: 2023788-19-2
Sequence (Linear): Y-Ahx-HGEGTFTSDLSKQMEEEAVRLFIEWLMNTKRNRNNIA-NH₂ (with fatty acid side chain)
Modifications: C20 fatty diacid moiety via γ-glutamic acid linker at Lys20
Structure Type: Synthetic linear peptide, 39 amino acids
Pharmacological Classification
Tirzepatide is a dual incretin mimetic that acts as a balanced agonist of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor and a biased agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor, both of which are class B G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs).
Mechanism of Action
- GIPR Activation: Enhances insulin secretion and lipogenesis in adipocytes.
- GLP-1R Activation: Inhibits glucagon, delays gastric emptying, and reduces appetite via CNS.
- Signaling: Activates cAMP via Gs proteins; exhibits GLP-1R biased agonism favoring cAMP over β-arrestin recruitment.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Tirzepatide shows functionally selective (biased) agonism at GLP-1R and GIPR:
- GLP-1R: Compared to native GLP-1, tirzepatide demonstrates significantly reduced β-arrestin recruitment, favoring prolonged cAMP signaling and decreased receptor internalization. This may contribute to sustained therapeutic activity and reduced desensitization.
- GIPR: Tirzepatide retains strong Gs-coupled cAMP activation with moderate β-arrestin recruitment, aligning closely with endogenous GIP signaling dynamics.
Comparative β-Arrestin Profile
| Receptor | Native Ligand | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Tirzepatide Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1R | GLP-1 | High | Low (biased toward cAMP) |
| GIPR | GIP | Moderate | Similar |
References: Lucey M et al., J Biol Chem 2020;295(45):15777–89. Willard FS et al., Cell Reports 2020;33(6):108293.
Molecular Engineering
Fatty acid conjugation increases albumin binding and plasma half-life. Sequence design includes DPP-IV resistance and selective receptor engagement with altered pharmacodynamics.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Elimination: Primarily proteolytic cleavage; renal excretion of fragments.
- Plasma Protein Binding: ~99%, primarily albumin
- Half-Life: ~5 days
Biological Effects
Modulates pancreatic hormone secretion, appetite, and adipocyte metabolism. Sustained receptor signaling contributes to glycemic control and weight reduction in preclinical models.
Preclinical Evidence
Demonstrated superior metabolic outcomes compared to GLP-1 monotherapy in db/db and high-fat diet models. Dual receptor activation provides enhanced insulinotropic response and fat mass reduction.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized powder
- Solubility: Sterile water, acetate buffer, DMSO (analytical prep)
- Storage: –20°C, protected from light and moisture
- Reconstitution pH Range: 4.0–6.0 preferred
Comparative Mechanistic Summary
| Parameter | GIP (native) | GLP-1 (native) | Tirzepatide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor Affinity | High (GIPR) | High (GLP-1R) | Dual, moderate |
| β-arrestin Recruitment | Moderate | High | Low (GLP-1R) |
| Receptor Internalization | Yes | Rapid | Delayed |
| Half-life | Minutes | Minutes | ~5 days |
| Albumin Binding | None | None | Strong |
References
- Yabe D, Seino Y. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011;107(2):248–256.
- Lucey M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(45):15777–15789.
- Willard FS, et al. Cell Reports. 2020;33(6):108293.
- Coskun T, et al. Diabetes. 2018;67(Suppl 1):64-LB.
- Knudsen LB, Lau J. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:155.
- Secher A, et al. Brain Res. 2014;1587:87–93.
- Finan B, et al. Cell Metab. 2021;33(1):77–91.
- Zhao P, et al. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6921.