Survodutide – Dual GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist
Chemical Identity
Chemical Name: Survodutide Acetate
Molecular Formula: C₂₂₁H₃₄₂N₄₆O₆₈
Molecular Weight: ~4740.5 Da
CAS Number: 2494517-62-2
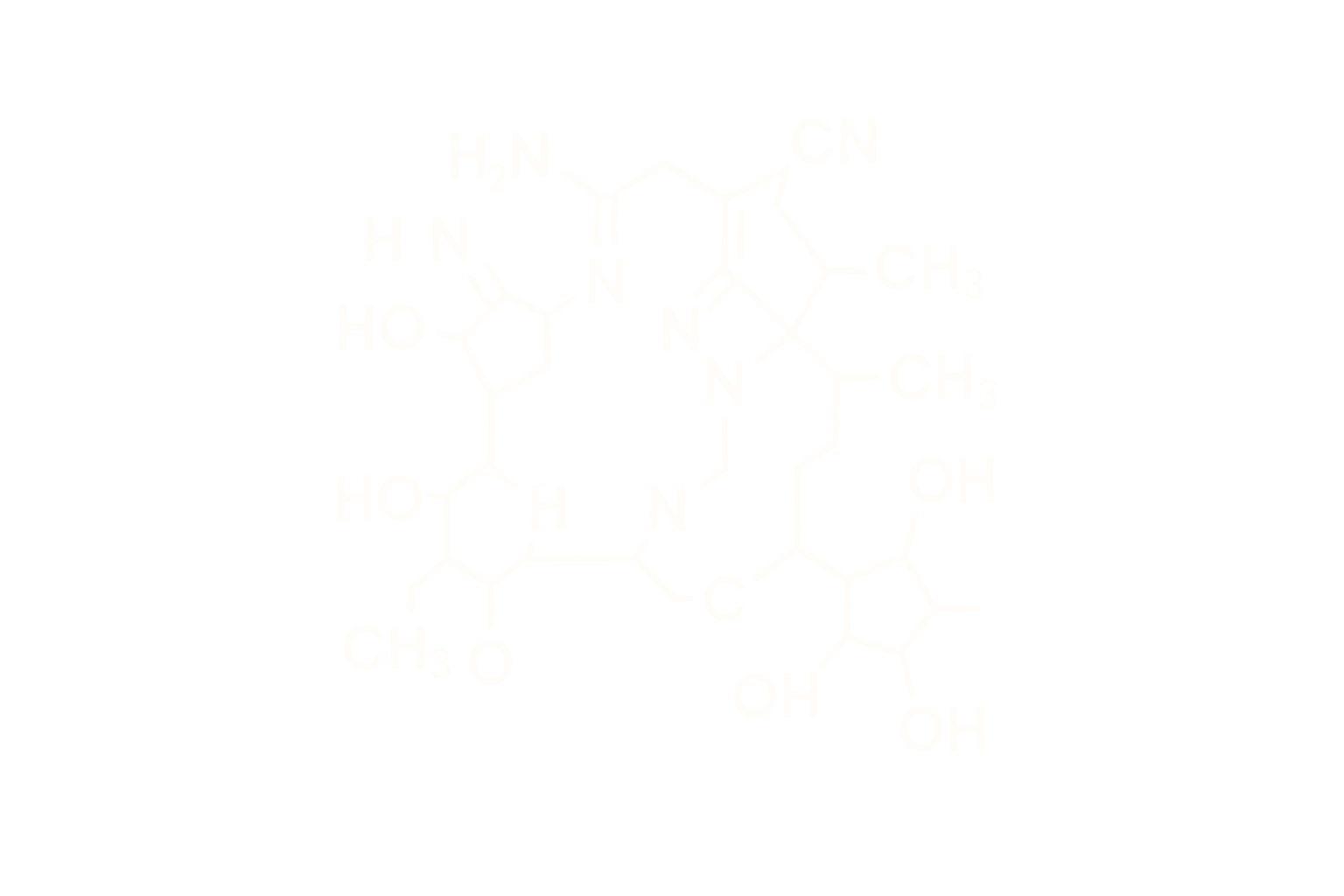
Sequence (Linear): H-His-Ser-Asp-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Val-Ser-Ser-Tyr-Leu-Glu-Gly-Gln-Ala-Ala-Lys-Glu-Phe-Ile-Ala-Trp-Leu-Val-Lys-Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe-Glu-Glu-Glu-Gln-Ala-Ala-Lys-NH₂
Modifications: C18 fatty diacid via linker attached to Lys20
Structure Type: Synthetic linear peptide, 39 amino acids
Pharmacological Classification
Survodutide is a dual agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and the glucagon receptor (GCGR). It is under investigation for the treatment of obesity and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, formerly NASH).
Mechanism of Action
- GLP-1R Activation: Promotes glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon, slows gastric emptying, and induces satiety.
- GCGR Activation: Increases energy expenditure, lipolysis, and hepatic fatty acid oxidation.
- Synergistic Effect: GLP-1R and GCGR co-activation induces weight loss via both appetite suppression and increased metabolic output.
- Signaling Pathways: Both receptors signal via Gs proteins to activate cAMP pathways; Survodutide demonstrates high potency in both receptor contexts.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Survodutide exhibits receptor-specific β-arrestin recruitment behavior, contributing to its functional selectivity:
- GLP-1 Receptor (GLP-1R): Acts as a biased agonist with reduced β-arrestin recruitment compared to native GLP-1. This promotes sustained Gs-mediated cAMP signaling and limits receptor internalization, potentially improving receptor responsiveness over time.
- Glucagon Receptor (GCGR): Demonstrates moderate β-arrestin recruitment, comparable to endogenous glucagon, balancing cAMP generation with receptor trafficking dynamics.
Comparative β-Arrestin Profile
| Receptor | Native Ligand | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Survodutide Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1R | GLP-1 | High | Low (biased toward cAMP) |
| GCGR | Glucagon | Moderate | Similar |
Reference: Brandt SJ et al., Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023;22(3):199–216.
Molecular Engineering
Survodutide is structurally modified with a fatty acid side chain to extend half-life via albumin binding. Substitutions increase GCGR affinity while preserving GLP-1R activity, balancing weight-loss efficacy and glycemic control.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Elimination: Primarily via proteolysis followed by renal clearance of fragments.
- Plasma Protein Binding: High (albumin-mediated)
- Half-Life: ~5–6 days (based on preclinical models and Phase 1 data)
Biological Effects
GLP-1R activation reduces food intake and improves insulin secretion, while GCGR activation promotes energy utilization and hepatic lipid metabolism. This dual action supports reductions in adiposity and liver fat content.
Preclinical Evidence
In diet-induced obese (DIO) rodent models, Survodutide induced significant weight loss, improved lipid panels, and reduced hepatic steatosis. In non-human primates, it outperformed GLP-1R monotherapy in reducing total fat mass.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized powder
- Solubility: Water, low-pH buffers, DMSO (analytical)
- Storage: –20°C; dry, light-protected environment
- Reconstitution pH: 4.0–5.5 recommended for structural stability
Comparative Mechanistic Summary
| Parameter | GLP-1 (native) | Glucagon (native) | Survodutide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor Affinity | High (GLP-1R) | High (GCGR) | Dual, optimized |
| cAMP Signaling | Strong | Strong | Balanced dual |
| Metabolic Effect | Appetite suppression | Energy expenditure | Both |
| Half-Life | Minutes | Minutes | ~5–6 days |
| Albumin Binding | None | None | Yes |
References
- Tillner J, et al. Cell Reports Medicine. 2023;4(1):100887.
- Könner AC, et al. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:672923.
- Khera T, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(12):2912–2928.
- Brandt SJ, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023;22(3):199–216.