Semax – Synthetic ACTH(4–10) Analog with Neurotropic and Nootropic Properties
Chemical Identity
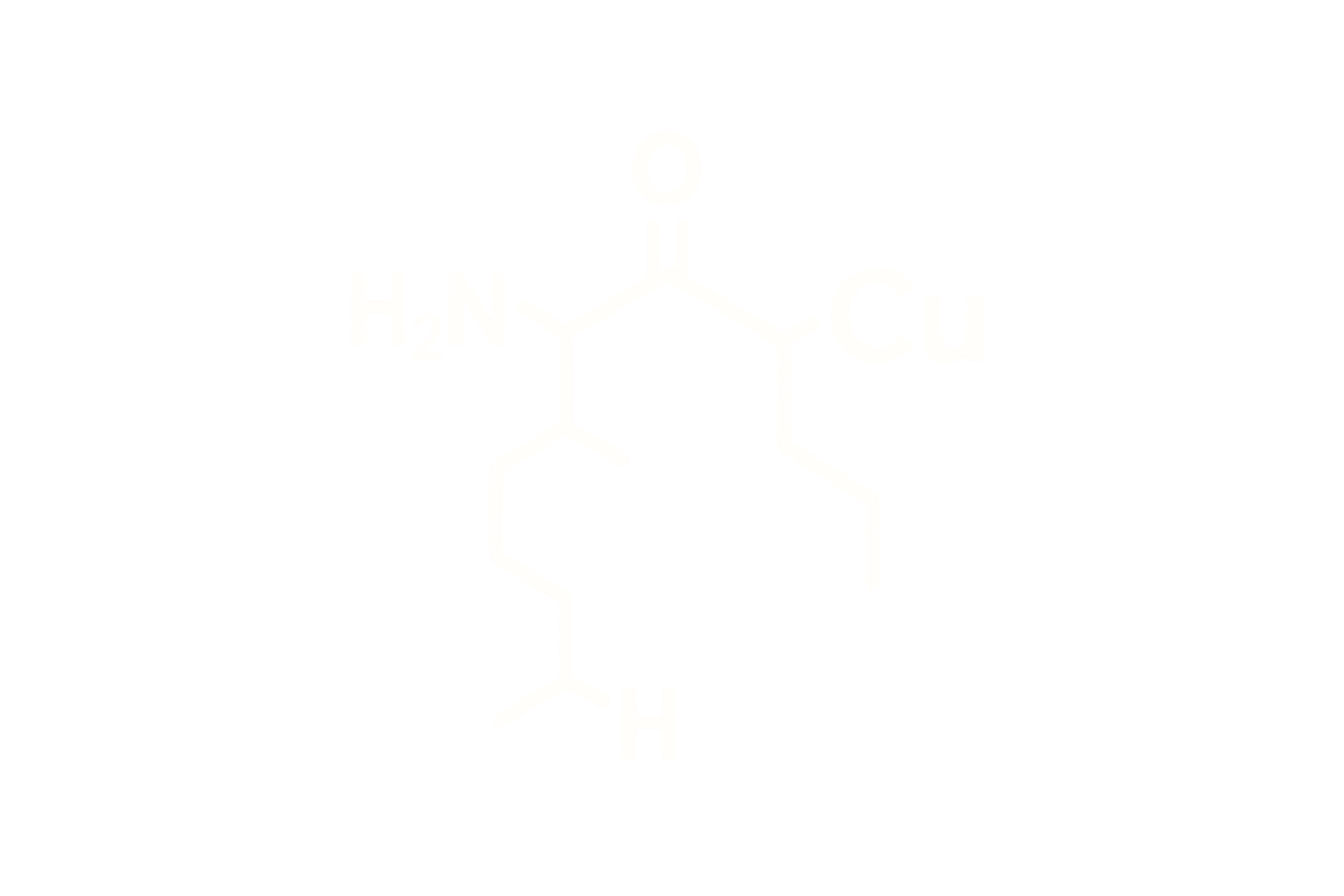
Chemical Name: L-Methionyl-L-α-glutamylhistidyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-prolylglycyl-L-proline
Synonyms: Semax; MEHFPGP; ACTH(4–10) analog
Molecular Formula: C₃₇H₅₁N₉O₁₀S
Molecular Weight: 813.93 g/mol
CAS Number: 80714-61-0
Sequence: Met-Glu-His-Phe-Pro-Gly-Pro
Structure Type: Synthetic heptapeptide derived from the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) fragment (4–10)
Pharmacological Classification
Semax is a **non-hormonal neuropeptide** and analog of ACTH(4–10), developed to exhibit **neuroprotective**, **nootropic**, and **neurorestorative** properties without glucocorticoid stimulation. It is approved in Russia for use in stroke, optic nerve ischemia, cognitive disorders, and neurodegeneration.
Mechanism of Action
- BDNF Induction: Upregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB receptor signaling, especially in hippocampal and cortical neurons.
- Monoamine Modulation: Enhances dopaminergic and serotonergic tone via regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase and monoamine oxidase expression.
- NF-κB Suppression: Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β), particularly in ischemic or oxidative injury.
- NRF2 Antioxidant Pathway: Increases expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes (e.g., SOD2, GPx, catalase).
- Neurovascular Support: Improves angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and mitochondrial stabilization in damaged neural tissue.
- Epigenetic Remodeling: Alters expression of neuroplasticity- and stress-related genes via chromatin and histone modifications.
Neurotropic Signaling Summary
| Target Pathway | Effect of Semax | Receptor or System |
|---|---|---|
| BDNF/TrkB | Upregulation of neurotrophic signaling | TrkB (tyrosine kinase receptor) |
| NF-κB | Suppression of inflammatory transcription | Non-GPCR intracellular pathway |
| NRF2 | Antioxidant gene activation | Nuclear transcription factor |
| Dopamine/Serotonin Systems | Elevated monoaminergic tone | Transporter modulation and synthesis control |
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Semax is not a GPCR agonist and does not exhibit β-arrestin recruitment. Its mechanism is nuclear, enzymatic, and transcriptional rather than membrane-receptor-mediated.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Route: Intranasal (primary), subcutaneous (investigational)
- Bioavailability: ~65–75% via intranasal administration
- Plasma Half-Life: ~20 minutes (short); however, downstream effects persist 12–24 hours
- Distribution: Rapid CNS penetration via olfactory epithelium
- Excretion: Primarily renal via peptidase-cleaved fragments
Biological Effects
Improves cognitive function, learning, attention, and memory. Promotes recovery after ischemic stroke and traumatic brain injury. Enhances neuronal survival, angiogenesis, and synaptogenesis. Reduces anxiety and stress markers in preclinical models without sedation.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, PBS, or dilute acidic buffers (pH 4.5–6.0)
- Storage: –20°C (lyophilized); 4°C reconstituted (≤14 days)
- Handling: Avoid light, moisture, and freeze-thaw cycles
References
- Dolotov OV, et al. J Neurochem. 2006;97(Suppl 1):82–86.
- Andreeva LA, et al. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2014;44(3):267–271.
- Gulyás B, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(5):689–705.
- Ashmarin IP, et al. Physiol Behav. 1995;57(4):819–823.
- PubChem CID 9811102 – Semax. PubChem