Semaglutide – GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
Chemical Identity
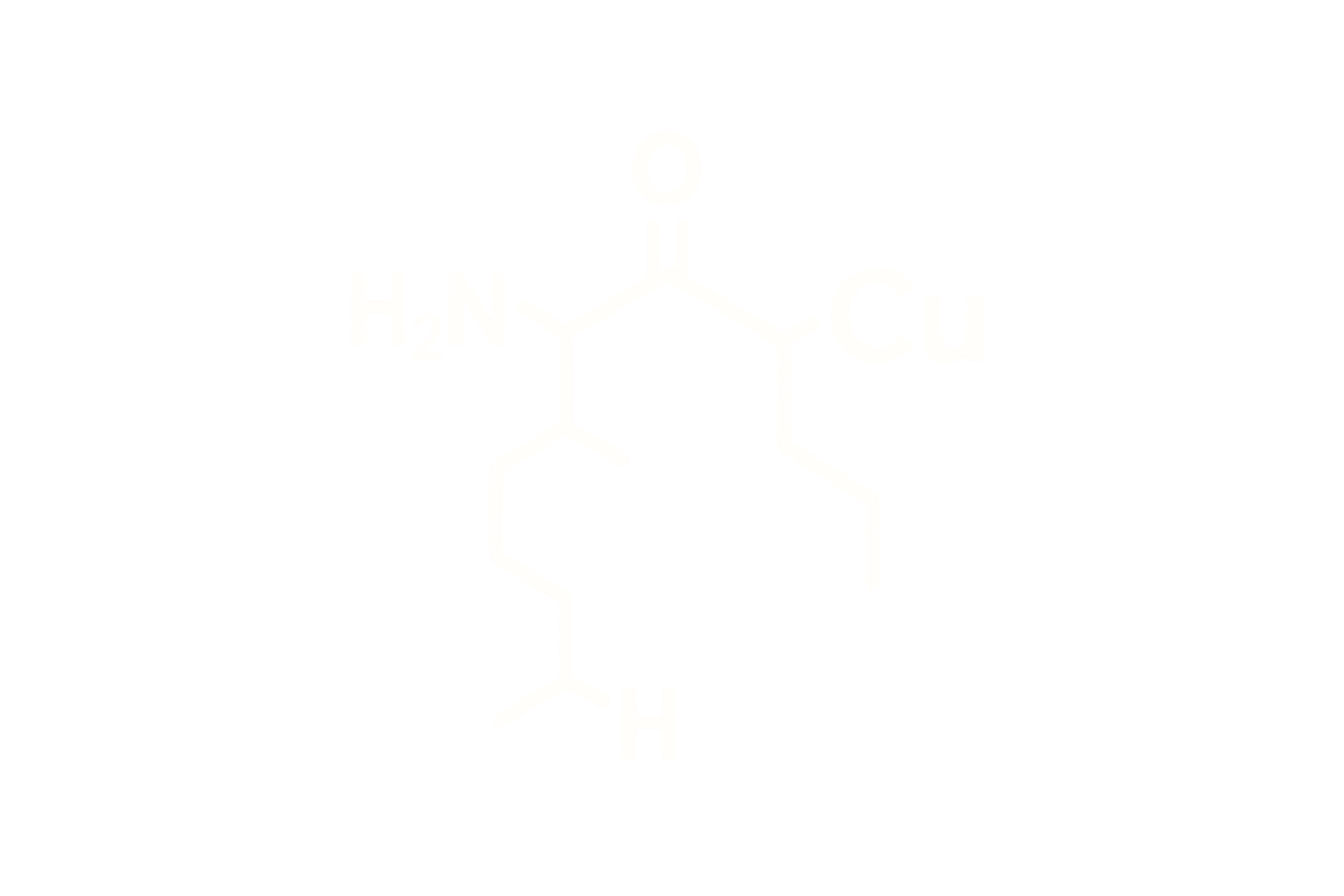
Chemical Name: Semaglutide Acetate
Molecular Formula: C₁₈₇H₂₉₁N₄₅O₅₉
Molecular Weight: ~4113.6 Da
CAS Number: 910463-68-2
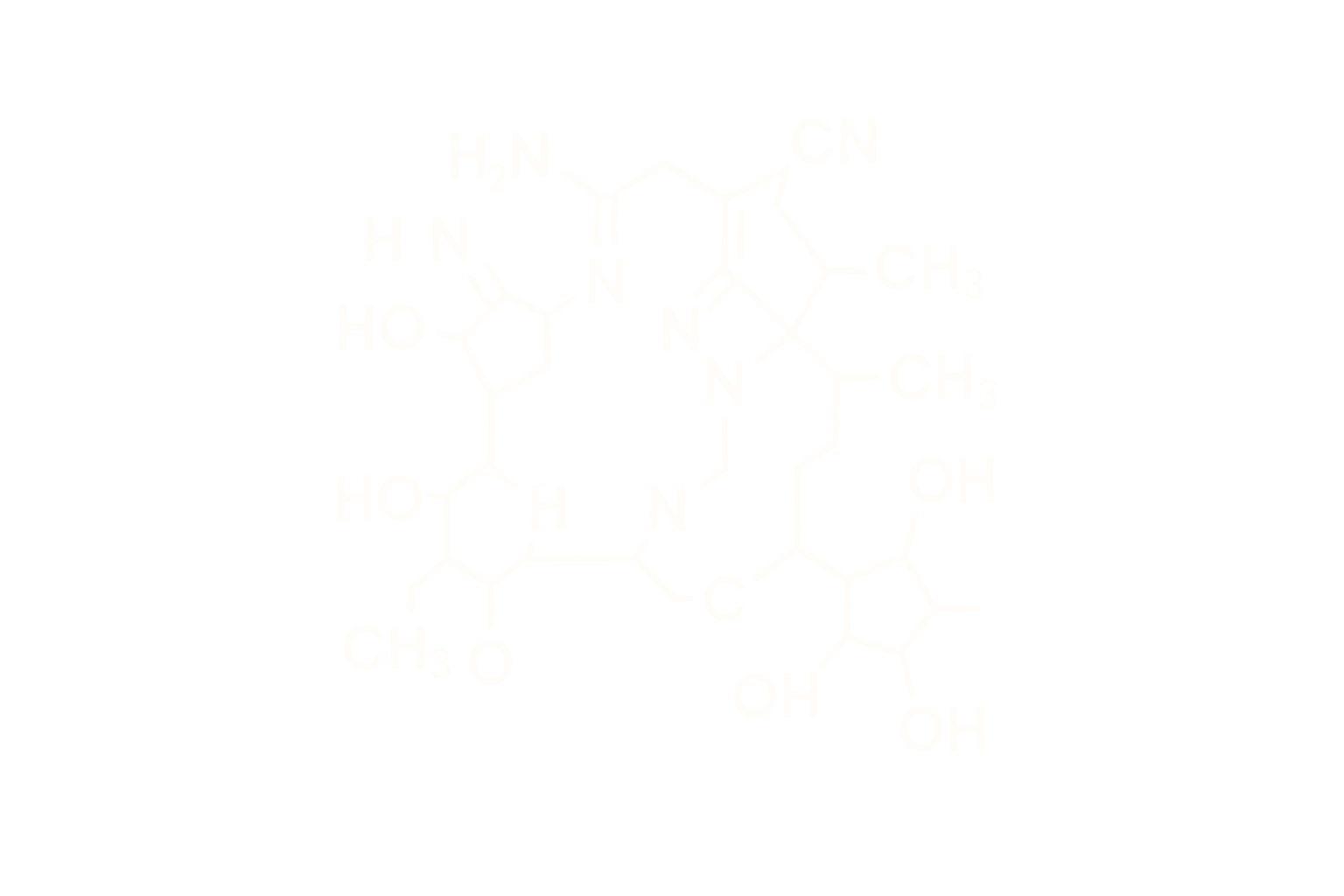
Sequence (Linear): H-Aib-Glu-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Asp-Val-Ser-Ser-Tyr-Leu-Glu-Gly-Gln-Ala-Ala-Lys(γGlu-2xOEG-C18 diacid)-Glu-Phe-Ile-Ala-Trp-Leu-Val-Arg-Gly-Arg-Gly-NH₂
Modifications: Aib at position 8, Lys acylated with C18 fatty diacid via glutamic acid and OEG linker
Structure Type: GLP-1(7-37) analog with extended half-life via albumin binding
Pharmacological Classification
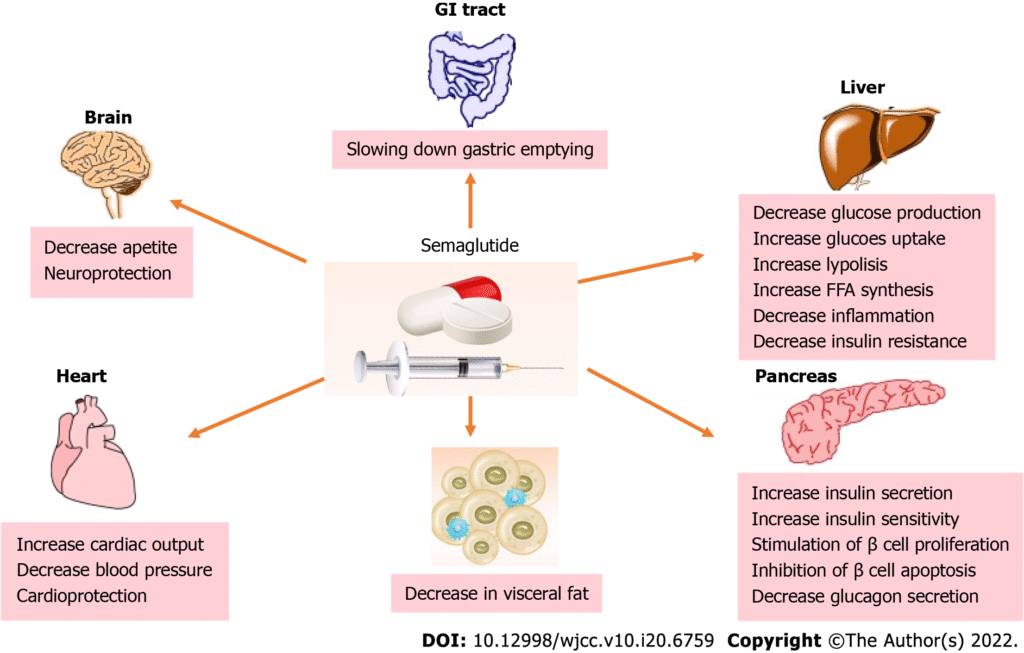
Semaglutide is a potent, long-acting agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), designed for metabolic regulation including glycemic control and appetite suppression.
Mechanism of Action
- GLP-1R Activation: Stimulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, delays gastric emptying, and reduces appetite via central pathways.
- Signaling: Acts via Gs-coupled activation of adenylate cyclase → increased intracellular cAMP → PKA activation and insulin gene transcription.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Semaglutide functions as a biased GLP-1R agonist:
- GLP-1R: Compared to native GLP-1, semaglutide exhibits reduced β-arrestin recruitment, favoring sustained cAMP signaling over receptor internalization and desensitization.
- This profile may enhance pharmacodynamic durability and mitigate tachyphylaxis during prolonged exposure.
Comparative β-Arrestin Profile
| Receptor | Native Ligand | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Semaglutide Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1R | GLP-1 | High | Reduced (biased toward cAMP) |
References: Jones B et al., Cell 2018;175(3):654–665. Willard FS et al., Cell Reports 2020;33(6):108293.
Molecular Engineering
Substitution of Aib (α-aminoisobutyric acid) at position 8 and acylation at Lys26 with a fatty diacid chain extend plasma half-life and protect from enzymatic degradation by DPP-IV.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Elimination: Primarily renal clearance of peptide fragments following proteolysis
- Plasma Protein Binding: >99% (albumin)
- Half-Life: ~160 hours (6–7 days)
Biological Effects
Reduces fasting plasma glucose, enhances β-cell responsiveness, and suppresses appetite by acting on hypothalamic POMC/CART neurons and brainstem GLP-1R sites.
Preclinical Evidence
In rodent and non-human primate models, semaglutide reduced body weight, visceral fat, and HbA1c more effectively than native GLP-1 or liraglutide. Demonstrates dose-proportional exposure and strong metabolic improvements across species.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized powder
- Solubility: Water, acidic buffer (pH 4–6), DMSO (analytical)
- Storage: –20°C, light and moisture protected
- Reconstitution pH: 4.5–5.5 preferred
Comparative Mechanistic Summary
| Parameter | GLP-1 (native) | Semaglutide |
|---|---|---|
| Receptor Affinity | High | High |
| β-arrestin Recruitment | High | Reduced |
| Receptor Internalization | Rapid | Slower |
| Half-life | ~2 min | ~6–7 days |
| Albumin Binding | No | Yes |
References
- Jones B, et al. Cell. 2018;175(3):654–665.e16.
- Willard FS, et al. Cell Reports. 2020;33(6):108293.
- Kapitza C, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(2):200–206.
- Knudsen LB, Lau J. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:155.
- Marre M, et al. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(7):821–828.