Selank – Synthetic Tuftsin Analog with Anxiolytic and Neuroregulatory Properties
Chemical Identity
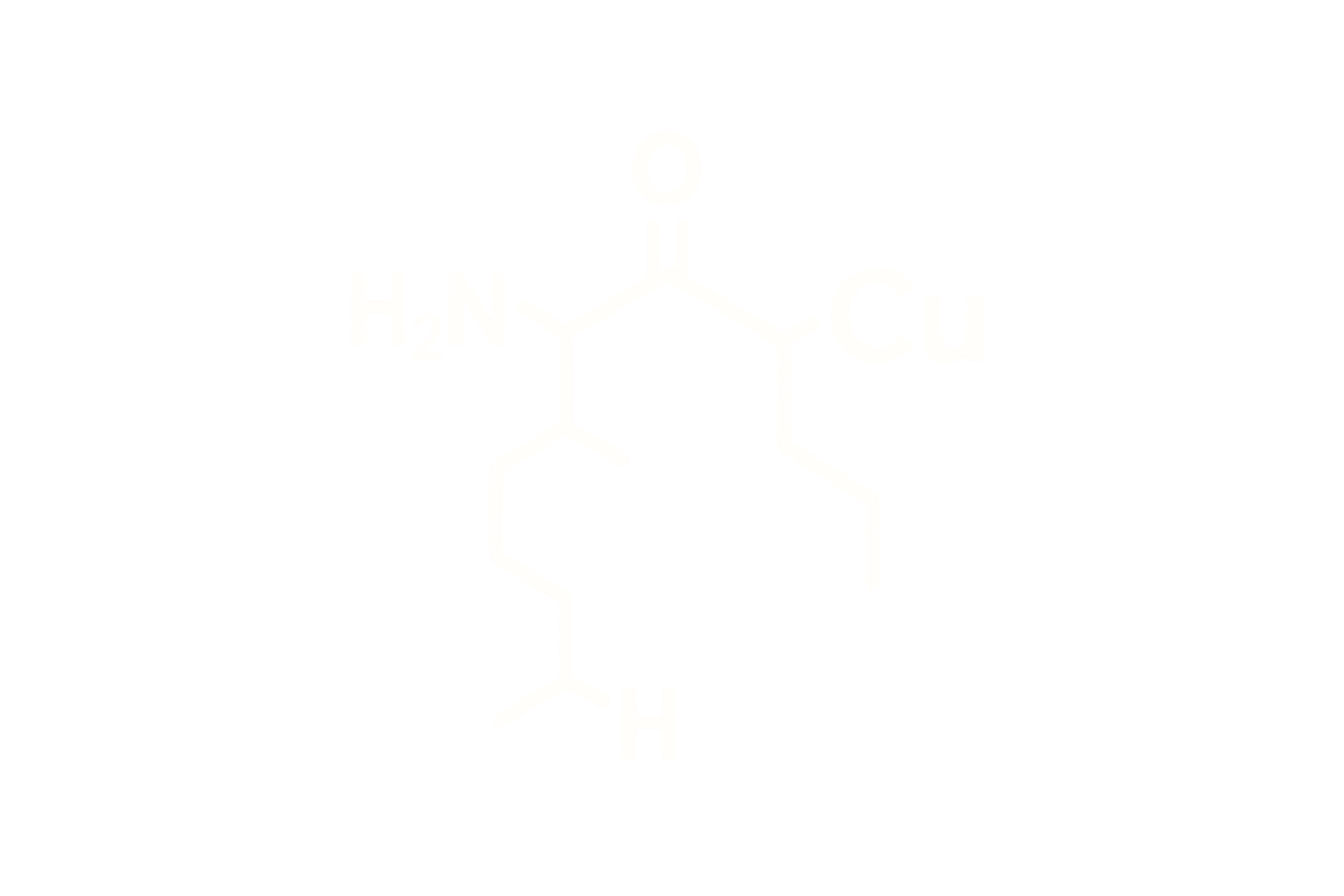
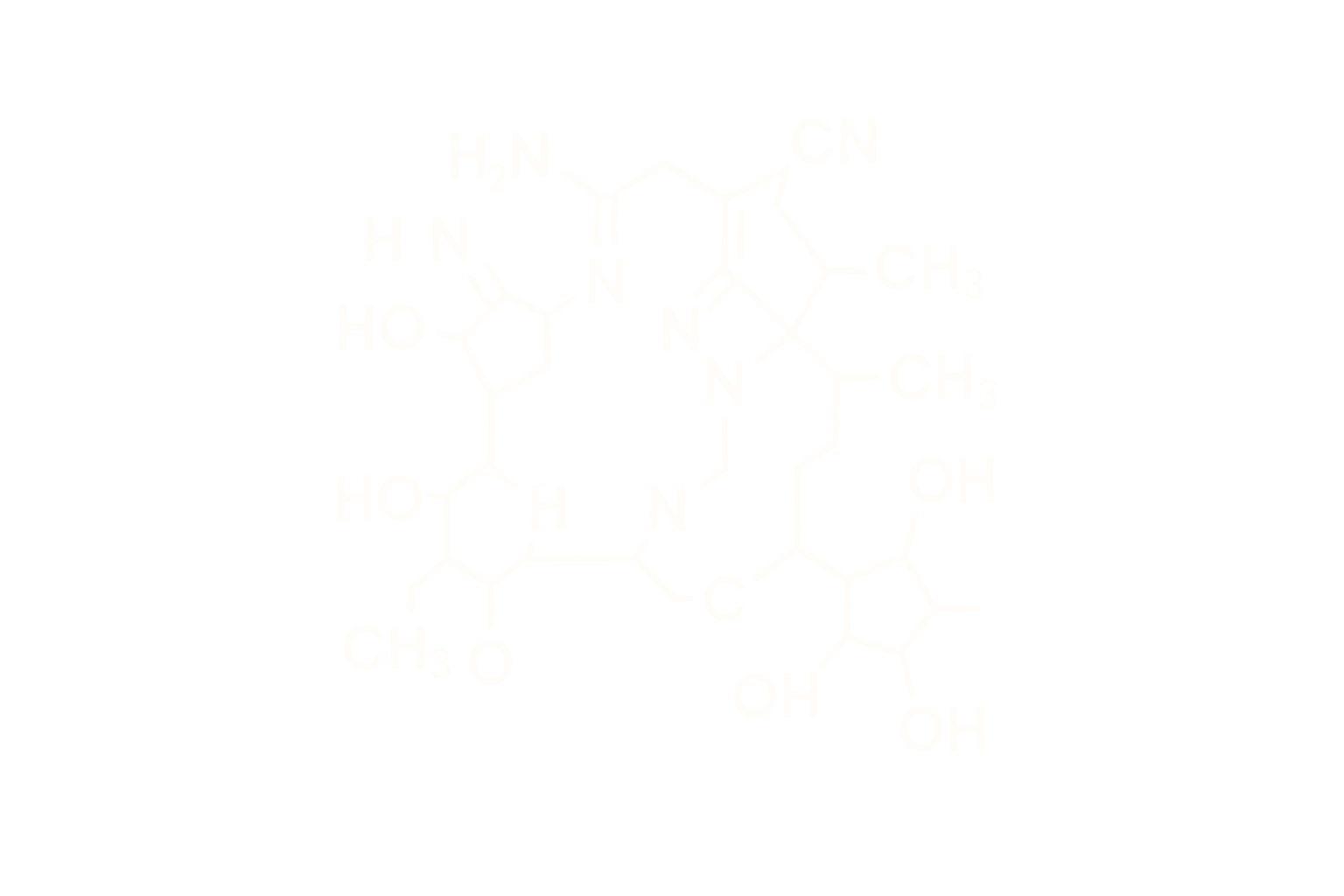
Chemical Name: L-Threonyl-L-lysyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycyl-L-proline
Synonyms: Selank; Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg-Pro-Gly-Pro
Molecular Formula: C₃₃H₅₇N₁₁O₉
Molecular Weight: 751.87 g/mol
CAS Number: 129954-34-3
Structure Type: Synthetic heptapeptide based on tuftsin
Pharmacological Classification
Selank is a synthetic peptide analog of tuftsin with potent **anxiolytic**, **nootropic**, and **immunomodulatory** properties. It exerts effects via GABAergic, monoaminergic, and cytokine-regulatory mechanisms, with no sedative, addictive, or withdrawal effects. Developed in Russia, it is used clinically for anxiety and cognitive impairment.
Mechanism of Action
- GABAergic Modulation: Enhances GABAA receptor activity, promoting anxiolysis without sedation.
- Monoamine Regulation: Stabilizes dopamine and serotonin turnover and receptor sensitivity.
- BDNF Upregulation: Increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in cortex and hippocampus.
- Cytokine Balancing: Suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6) while enhancing anti-inflammatory mediators (e.g., IL-10).
- Enkephalinase Inhibition: May reduce degradation of endogenous neuropeptides related to stress and affect.
Neurotropic Signaling Summary
| Target Pathway | Effect of Selank | Receptor/System |
|---|---|---|
| GABAergic Tone | Enhanced inhibitory signaling | GABAA modulation |
| BDNF Expression | Upregulation in hippocampus | TrkB (indirect) |
| Cytokine Signaling | ↓ IL-6, ↑ IL-10 | Neuroimmune interface |
| Monoamine Turnover | Stabilization of dopamine/serotonin levels | Indirect (non-receptor-mediated) |
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Selank does not activate G protein-coupled receptors and is not associated with β-arrestin recruitment. Its signaling occurs via intracellular transcriptional pathways and neuromodulator stabilization.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Route of Administration: Intranasal (primary), subcutaneous (investigational)
- Bioavailability: ~70% via intranasal route; potentially higher with parenteral injection
- Half-Life: ~5–10 minutes in plasma; CNS effects may persist 4–6 hours post-administration
- Distribution: Rapid CNS penetration via olfactory and circulatory access; regional accumulation in hippocampus and cortex observed
- Metabolism: Proteolytic cleavage by peptidases; renal excretion of fragments
Biological Effects
Selank exerts rapid anxiolytic effects, enhances cognitive function, and modulates immune activity. It has been shown to increase attention and memory, reduce IL-6 in stress models, and normalize behavior in rodent models of anxiety without sedation or dependence.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, 0.9% saline, or acetate buffer (pH 4.5–6.0); sterile solvents recommended for injectable applications
- Storage: Store lyophilized powder at –20°C. After reconstitution, refrigerate (2–8°C) and use within 14 days
- Handling: Protect from light and moisture. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Use aseptic technique for injection
References
- Andreeva LA, et al. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2014;44(3):267–271.
- GABA, Selank, and Olanzapine affect gene expression in cortex. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:171.
- Khavinson V, et al. Peptides. 2003;24(5):659–665.
- Selank – Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selank