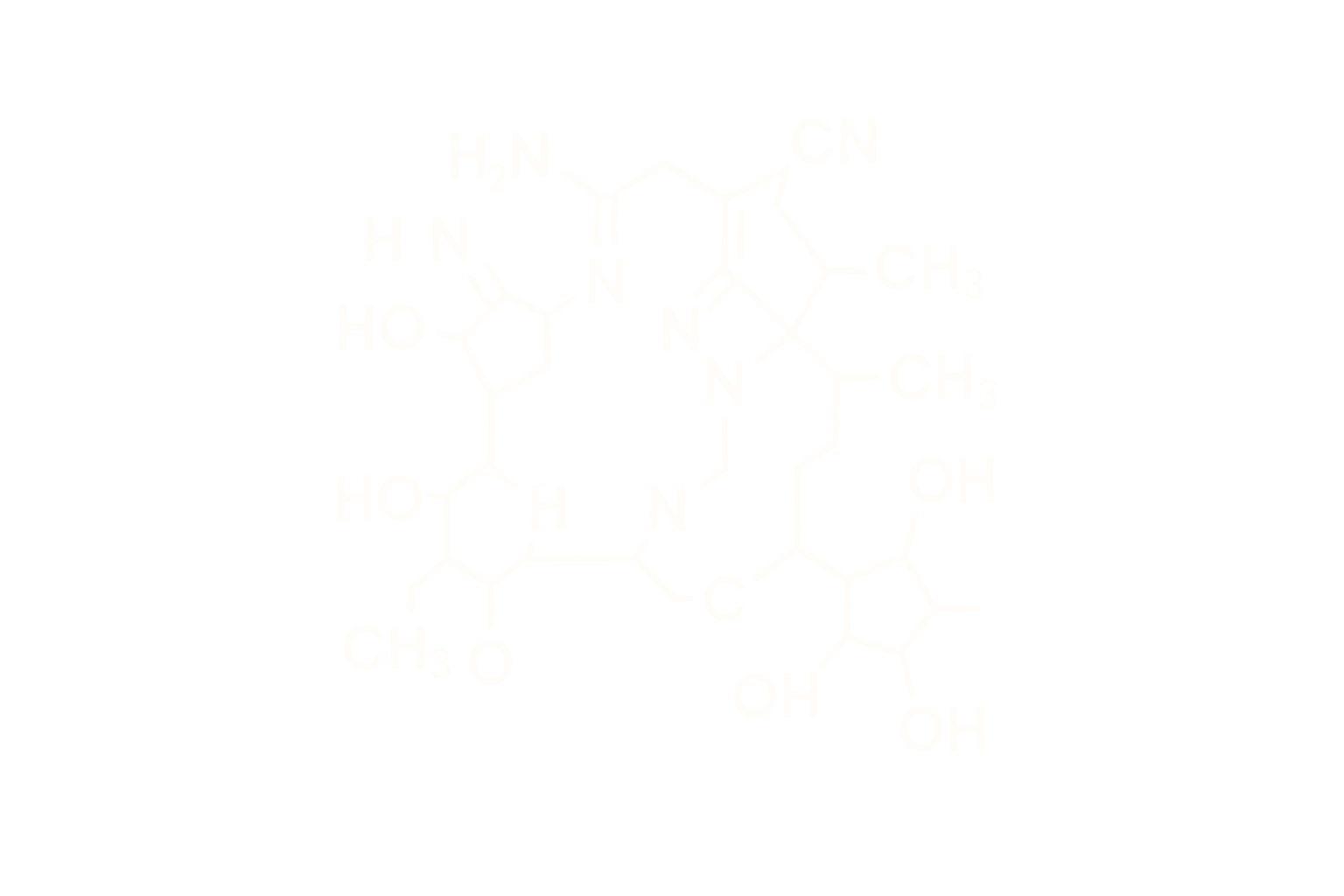
Melanotan 1 (Afamelanotide) – Synthetic α-MSH Analog & MC1R Agonist
Chemical Identity
Chemical Name: [Nle4, D-Phe7]-α-MSH; Afamelanotide
Synonyms: Melanotan I, MT-1, NDP-MSH, CUV1647
Molecular Formula: C78H111N21O19
Molecular Weight: 1646.85 Da
CAS Number: 75921-69-6
Sequence: Ac-Ser-Tyr-Ser-Nle-Glu-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val-NH2
Structure Type: Synthetic linear tridecapeptide analog of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)
Pharmacological Classification
Melanotan 1 is a **selective melanocortin receptor agonist**, primarily targeting the **MC1R** subtype. It is a synthetic analog of α-MSH, designed to induce melanogenesis and provide photoprotection. Afamelanotide has been approved for the treatment of erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP) in several regions, including the European Union and the United States.
Mechanism of Action
- MC1R Activation: Binds to melanocortin 1 receptors on melanocytes, stimulating eumelanin production, leading to increased skin pigmentation and photoprotection.
- Photoprotective Effects: Enhances the skin's defense against ultraviolet radiation by increasing melanin content, thereby reducing phototoxic reactions in conditions like EPP.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Exhibits anti-inflammatory effects through melanocortin receptor-mediated pathways, contributing to its therapeutic benefits in certain dermatological conditions.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Melanotan 1 functions via **G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)** mechanisms, specifically through MC1R activation. While detailed studies on β-arrestin recruitment are limited, its receptor activity suggests involvement of β-arrestin pathways in receptor desensitization and internalization processes.
Melanocortin Receptor Affinity Profile
| Receptor | Affinity | Physiological Role |
|---|---|---|
| MC1R | High | Pigmentation, anti-inflammatory responses |
| MC3R | Moderate | Energy homeostasis |
| MC4R | Moderate | Appetite regulation, sexual behavior |
| MC5R | Low | Exocrine gland function |
Pharmacokinetics
- Administration: Subcutaneous injection
- Bioavailability: High
- Time to Peak Concentration (Tmax): Approximately 1 hour
- Half-Life: Approximately 30 minutes; extended to ~15 hours with slow-release implant formulations
- Metabolism: Primarily hepatic
- Excretion: Minimal amounts recovered unchanged in urine; extensive metabolism suggests biliary or fecal elimination
Biological Effects
Clinical studies have demonstrated that Melanotan 1 effectively increases skin pigmentation, providing photoprotection for individuals with photosensitive conditions like EPP. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties contribute to its therapeutic potential in various dermatological disorders. Side effects are generally mild and may include nausea, flushing, and headache.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized powder
- Solubility: Soluble in sterile water; recommended concentration up to 0.6 mg/mL
- Storage: Store desiccated below –18°C; stable at room temperature for up to 3 weeks
- Reconstitution: Upon reconstitution, store at 4°C for 2–7 days; for extended storage, keep below –18°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
References
- Afamelanotide. DrugBank. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB04931
- Melanotan-I | C78H111N21O19 | CID 16164658. PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Melanotan-I
- Skin pigmentation and pharmacokinetics of melanotan-I in humans. PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9113347/
- Afamelanotide. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Afamelanotide