Mazdutide – Dual GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonist
Chemical Identity
Chemical Name: Mazdutide Acetate (also known as IBI362)
Molecular Formula: C₂₂₇H₃₆₄N₄₆O₆₇
Molecular Weight: ~4791.6 Da
CAS Number: 2416895-87-7
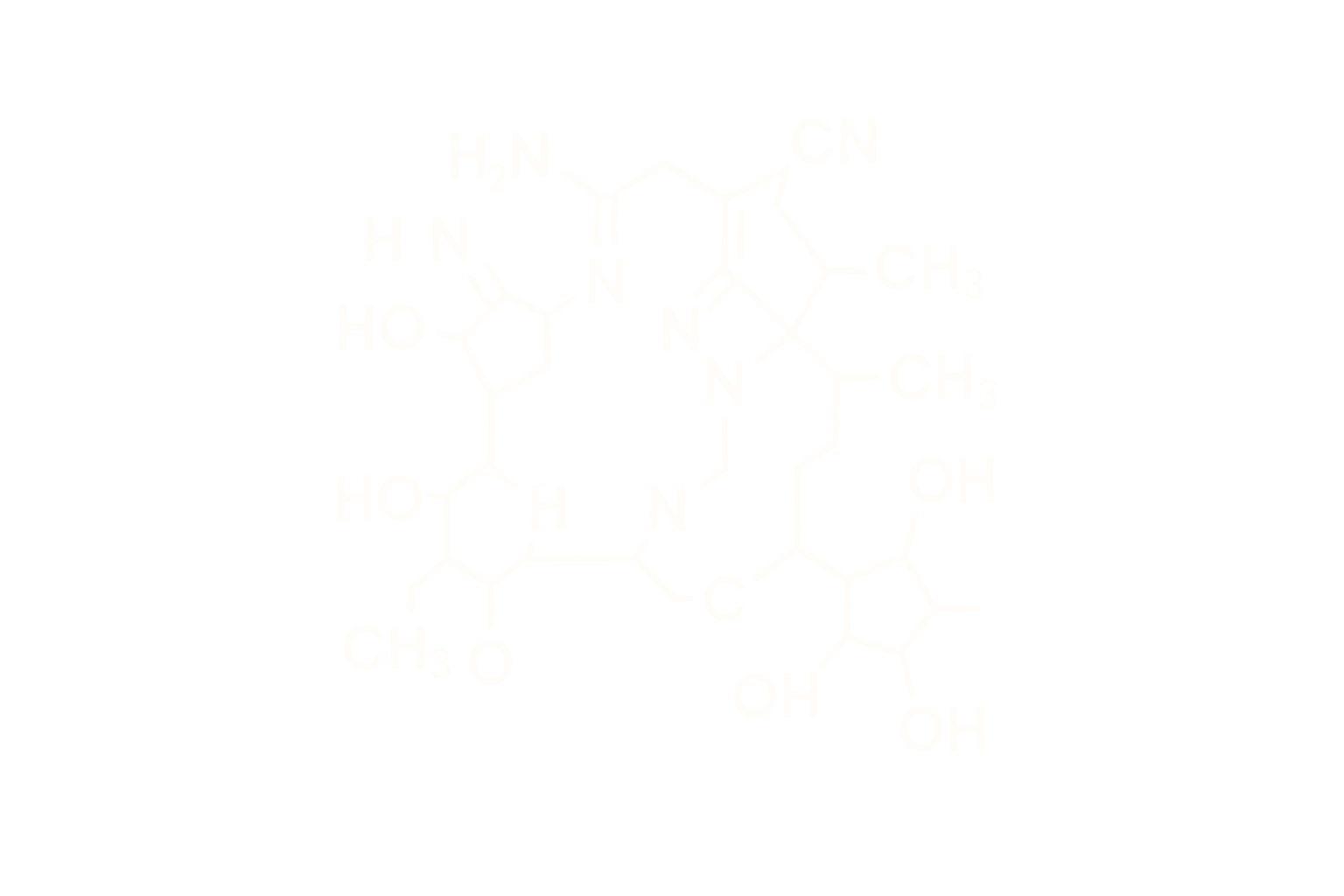
Sequence (Linear): GLP-1-based sequence with multiple amino acid substitutions and lipidation for prolonged activity
Modifications: C18 fatty diacid side chain conjugated via linker to lysine residue; engineered substitutions for enhanced dual GLP-1R/GCGR co-agonism
Structure Type: Synthetic 39-amino acid linear peptide, lyophilized acetate salt
Pharmacological Classification
Mazdutide is a **dual receptor agonist** that targets both the **glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R)** and the **glucagon receptor (GCGR)**. Developed by Innovent Biologics, it is under clinical investigation for obesity and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD/MASH).
Mechanism of Action
- GLP-1R Activation: Increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppresses glucagon, delays gastric emptying, and reduces appetite.
- GCGR Activation: Stimulates hepatic lipid oxidation, thermogenesis, and energy expenditure.
- Signal Transduction: Both receptors primarily signal through Gs protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP → PKA pathway.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Mazdutide exhibits receptor-specific bias in β-arrestin recruitment:
- GLP-1R: Displays low β-arrestin recruitment relative to native GLP-1, favoring cAMP signaling and limiting internalization.
- GCGR: Exhibits moderate β-arrestin recruitment, balancing receptor signaling and desensitization.
Comparative β-Arrestin Profile
| Receptor | Native Ligand | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Mazdutide Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1R | GLP-1 | High | Reduced (biased toward cAMP) |
| GCGR | Glucagon | Moderate | Moderate |
References: Lin L et al., eClinicalMedicine. 2023;62:102133. Willard FS et al., Cell Reports. 2020;33(6):108293.
Molecular Engineering
Modified with multiple substitutions to enhance dual receptor affinity. C18 fatty acid conjugation via a linker increases half-life and albumin binding. Designed to improve metabolic efficacy while reducing gastrointestinal side effects.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Elimination: Primarily via proteolysis; renal clearance of fragments
- Plasma Protein Binding: >99% (albumin-mediated)
- Half-Life: ~6–7 days
Biological Effects
Reduces body weight, appetite, and hepatic steatosis through GLP-1–mediated anorectic effects and GCGR-mediated energy expenditure. No hypoglycemia observed due to glucose-dependent insulinotropic activity.
Preclinical Evidence
In rodent and monkey models, Mazdutide significantly reduced food intake, body fat, liver triglycerides, and improved insulin sensitivity. Demonstrated robust synergy between GLP-1R and GCGR pathways.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized powder, acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, low-pH buffers (pH 4.0–6.0), DMSO for in vitro work
- Storage: –20°C, light- and moisture-protected
- Reconstitution pH: 4.5–5.5 recommended
Comparative Mechanistic Summary
| Parameter | GLP-1 | Glucagon | Mazdutide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor Targets | GLP-1R | GCGR | Both |
| β-arrestin Recruitment | High | Moderate | Low–Moderate |
| Half-Life | <5 minutes | ~10 minutes | ~6–7 days |
| Albumin Binding | No | No | Yes |
References
- Lin L, et al. eClinicalMedicine. 2023;62:102133.
- Zhou J, et al. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:944728.
- Willard FS, et al. Cell Reports. 2020;33(6):108293.
- Sun F, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(5):1363–1372.