Ipamorelin – Selective GHSR Agonist & Growth Hormone Secretagogue
Chemical Identity
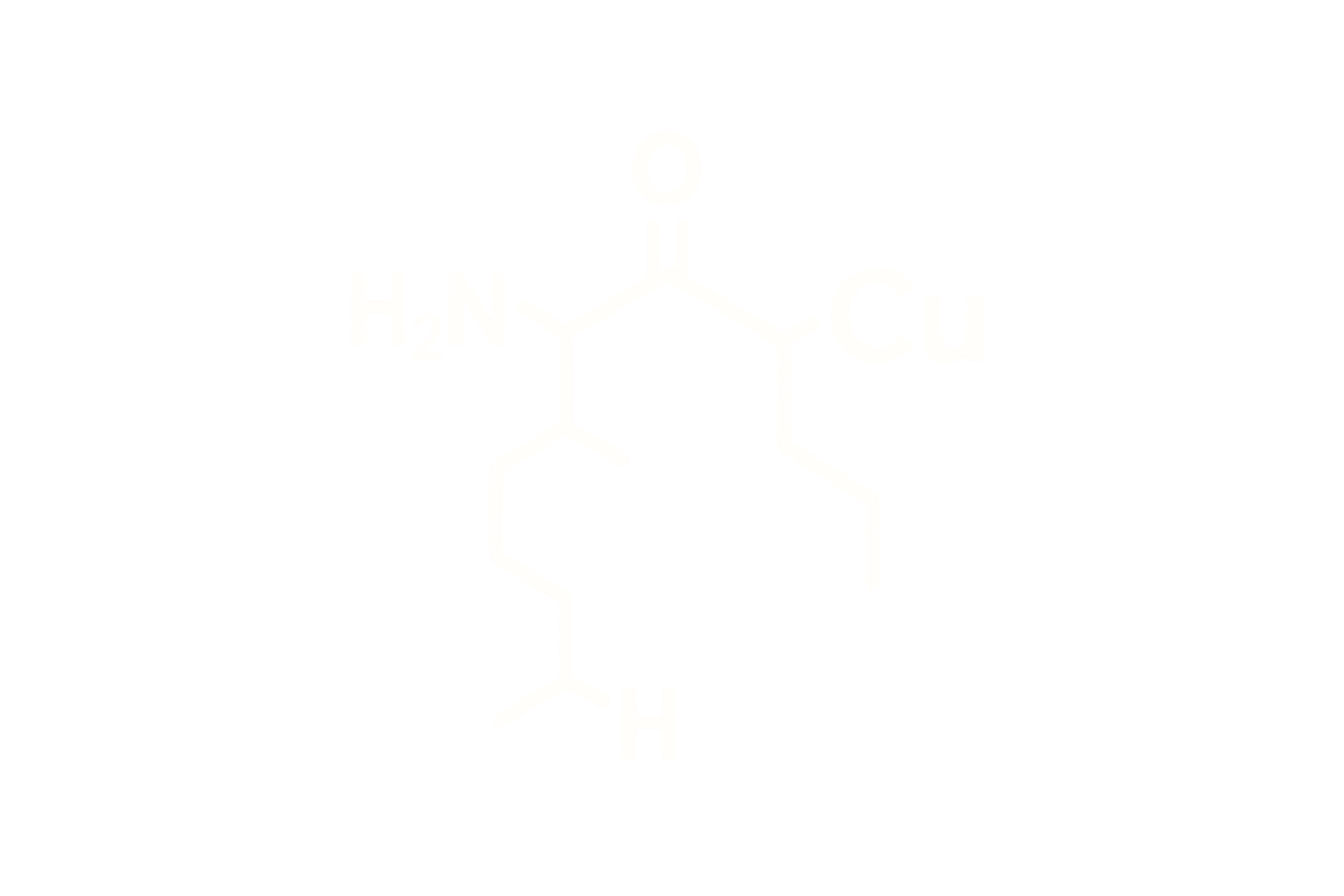
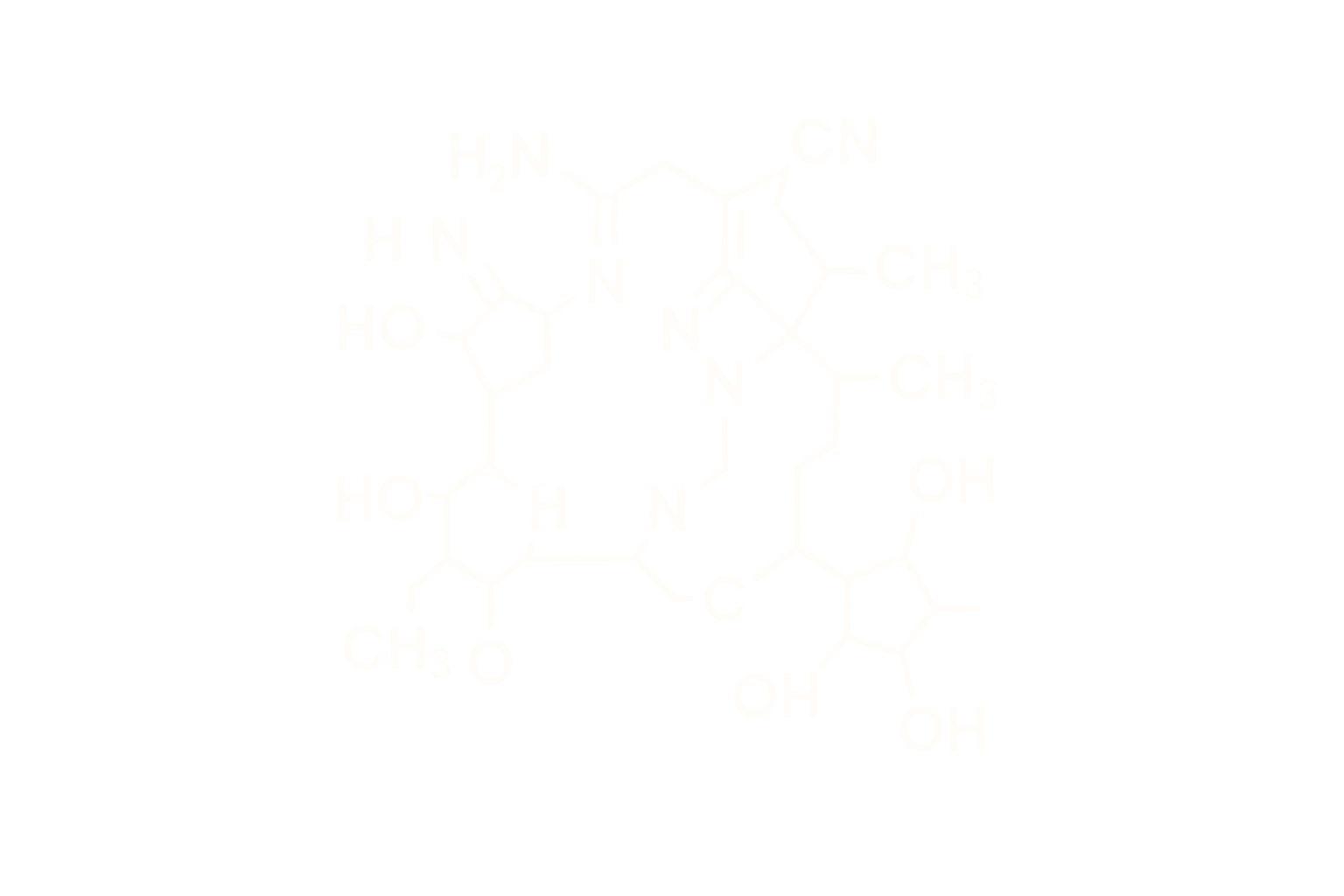
Chemical Name: Ipamorelin Acetate
Molecular Formula: C₃₈H₄₉N₉O₅
Molecular Weight: ~711.85 Da
CAS Number: 170851-70-4
Sequence (Linear): Aib-His-D-2-Nal-D-Phe-Lys-NH2
Structure Type: Synthetic pentapeptide mimetic and selective ghrelin receptor agonist (GHSR-1a)
Pharmacological Classification
Ipamorelin is a highly selective growth hormone secretagogue (GHS) that functions as an agonist of the ghrelin receptor, formally known as the growth hormone secretagogue receptor type 1a (GHSR-1a). Unlike earlier GHS peptides, it is noted for its selectivity, minimal off-target activity, and lack of effects on cortisol or prolactin secretion.
Mechanism of Action
- GHSR-1a Activation: Binds GHSR-1a in the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus to stimulate pulsatile growth hormone (GH) release.
- G-protein Signaling: Activates Gq and Gi/o-coupled signaling cascades involving IP3, DAG, and cAMP.
- Neuroendocrine Modulation: Enhances hypothalamic GHRH tone while suppressing somatostatin inhibition.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Ipamorelin exhibits low β-arrestin recruitment at the GHSR-1a receptor compared to other secretagogues like hexarelin or ghrelin. This signaling bias reduces receptor desensitization and internalization, supporting sustained GH release during chronic exposure.
GHSR-1a Receptor Bias Profile
| Ligand | GH Release | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Desensitization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghrelin | Strong | High | Rapid |
| Hexarelin | Strong | High | Marked |
| Ipamorelin | Moderate–Strong | Low | Minimal |
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Half-Life: ~2 hours (short-acting secretagogue)
- Administration Routes: Effective subcutaneously and intravenously in preclinical models
- Clearance: Hepatic and renal proteolytic degradation
Biological Effects
Promotes GH release without increasing ACTH, cortisol, or prolactin. Shown to support lean mass preservation, enhance recovery, and stimulate IGF-1 synthesis in preclinical settings. No evidence of insulin resistance, glycemic disruption, or aldosterone elevation.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, 0.01M HCl, saline, or dilute acetic acid
- Storage: –20°C; protect from light and moisture
- Reconstitution pH: 4.0–5.5 recommended
References
- Smith RG, et al. Endocrinology. 1997;138(11):5177–5183.
- Raun K, et al. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998;139(5):552–561.
- Camargos ST, et al. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2010;23(11):1133–1142.
- Moulin A, et al. Front Endocrinol. 2012;3:136.