GHRP-6 – Hexapeptide Ghrelin Receptor Agonist
Chemical Identity
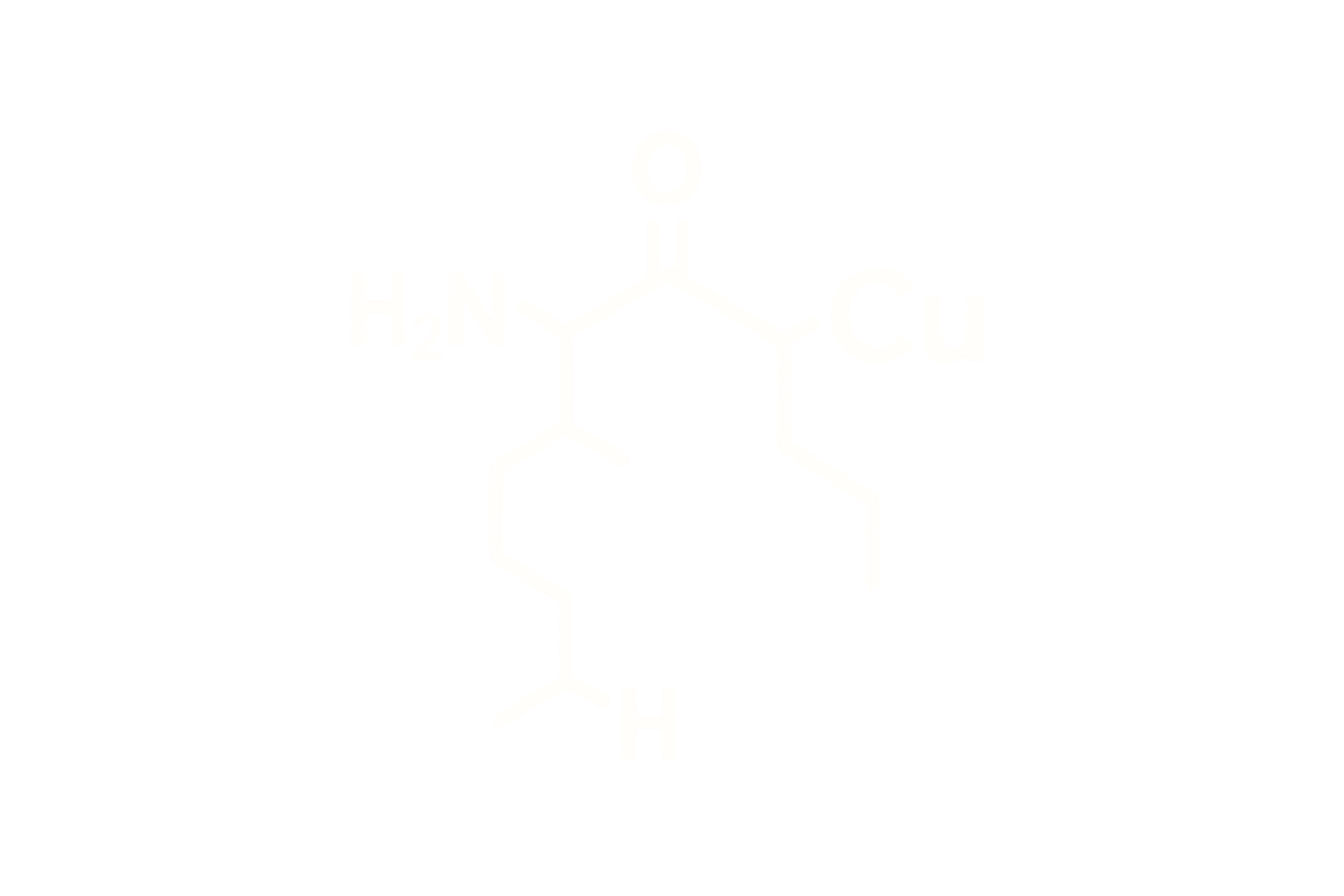
Chemical Name: Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-6 Acetate
Molecular Formula: C₄₆H₅₆N₁₂O₆
Molecular Weight: ~873.01 Da
CAS Number: 87616-84-0
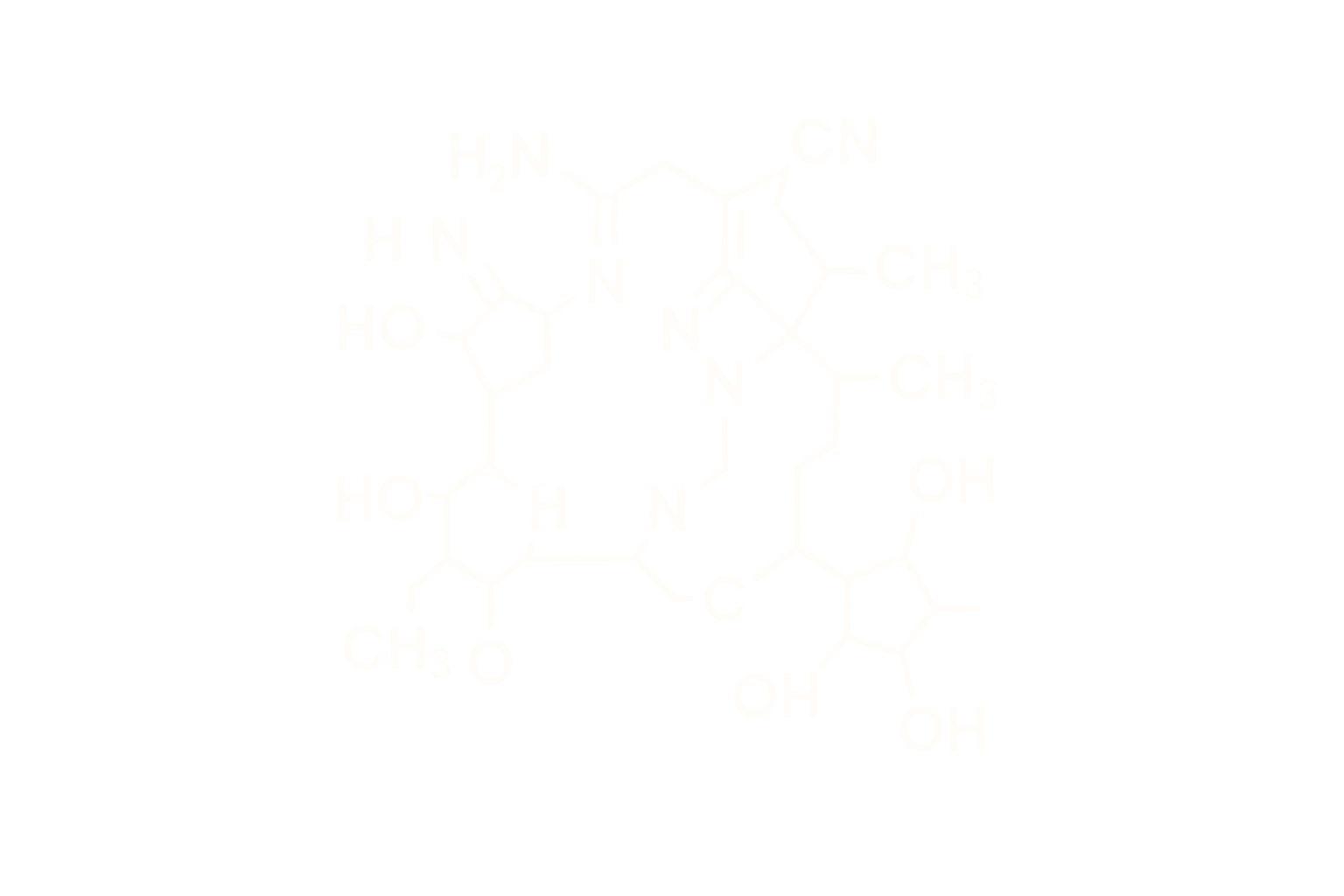
Sequence: His-D-Trp-Ala-Trp-D-Phe-Lys-NH2
Structure Type: Synthetic hexapeptide; ghrelin receptor (GHSR-1a) agonist
Pharmacological Classification
GHRP-6 is a first-generation **growth hormone secretagogue (GHS)** that binds and activates the **GHSR-1a (ghrelin receptor)**, stimulating pulsatile growth hormone (GH) release from anterior pituitary somatotrophs. It was among the earliest synthetic peptides developed to mimic the GH-releasing activity of ghrelin, with additional effects on appetite and metabolism.
Mechanism of Action
- GHSR-1a Activation: Binds to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor, triggering Gq and Gi/o-mediated intracellular signaling cascades.
- GH Release: Enhances pulsatile secretion of GH and synergizes with GHRH signaling pathways.
- Appetite Modulation: Promotes orexigenic effects by acting on hypothalamic neurons; mimics ghrelin in food intake models.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
GHRP-6 displays **moderate to high β-arrestin recruitment** at the GHSR-1a receptor, which contributes to receptor internalization and desensitization with chronic exposure. It is less biased than newer analogs like Ipamorelin, resulting in a stronger acute signal but reduced sustainability over time.
GHSR-1a Ligand Bias Comparison
| Ligand | GH Release | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Desensitization Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghrelin | Strong | High | Marked |
| GHRP-6 | Strong | Moderate–High | Moderate |
| Ipamorelin | Moderate–Strong | Low | Minimal |
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Half-Life: ~20–30 minutes (short-acting)
- Bioavailability: Effective subcutaneously and intravenously
- Clearance: Primarily via proteolytic degradation and renal excretion
Biological Effects
GHRP-6 increases plasma GH and IGF-1, stimulates appetite, promotes lean mass development, and supports tissue repair in preclinical models. Unlike Ipamorelin, it may elevate prolactin and cortisol due to less selective receptor interactions at higher concentrations.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, 0.01 M HCl, saline, or acetic acid
- Storage: –20°C; protect from light and humidity
- Reconstitution: pH 4.5–5.5 recommended for solution stability
References
- Smith RG, et al. Endocr Rev. 1997;18(5):621–645.
- Chen HY, et al. Endocrinology. 1996;137(12):5242–5249.
- Camargos ST, et al. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2010;23(11):1133–1142.
- van der Lely AJ, et al. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151 Suppl 1:S1–S9.