GHK-Cu – Copper Tripeptide Complex
Chemical Identity
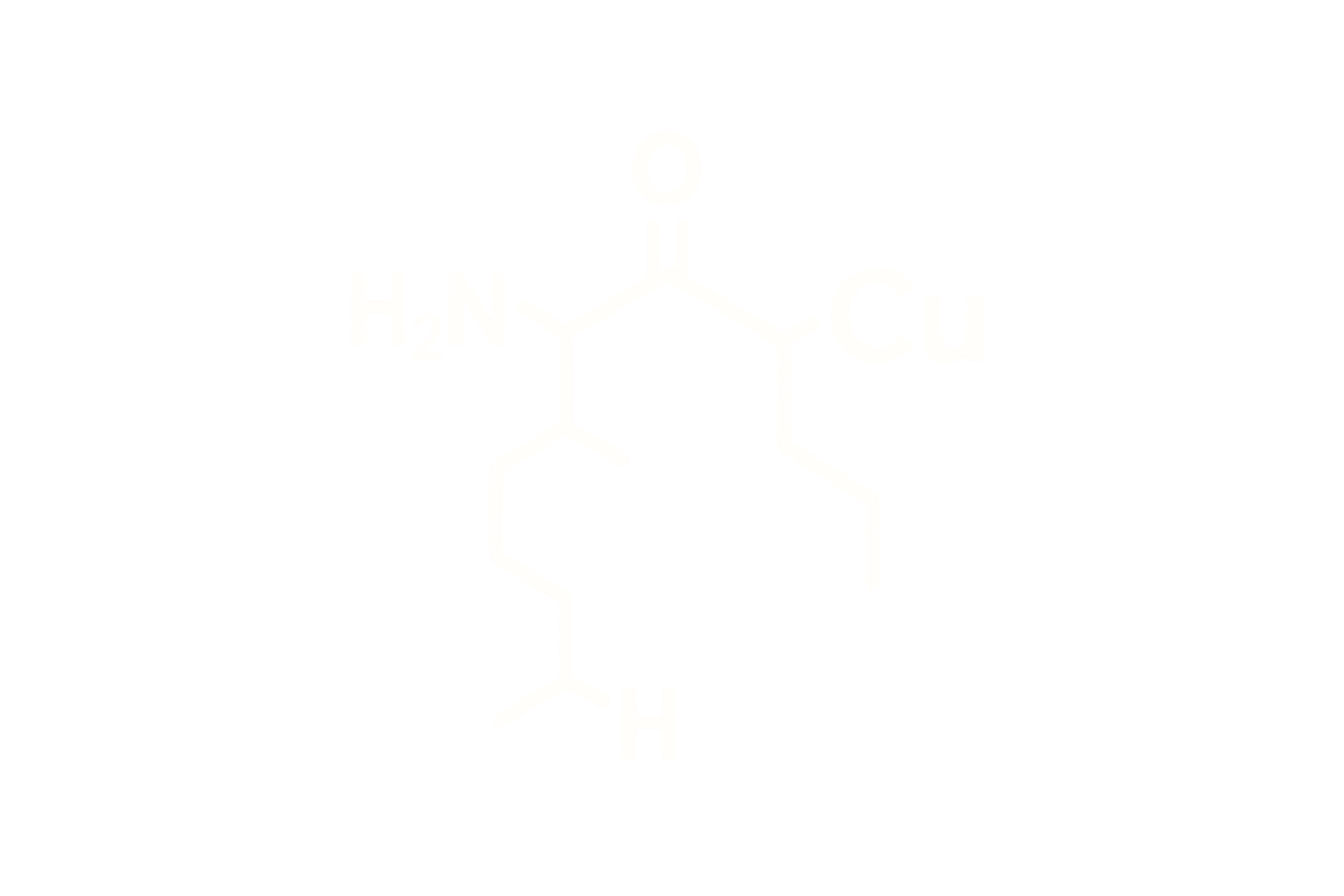
Chemical Name: Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine Copper(II) Complex
Synonyms: Copper Tripeptide-1, Prezatide Copper Acetate, Iamin
Molecular Formula: C₁₄H₂₄CuN₆O₄
Molecular Weight: ~403.9 Da
CAS Number: 49557-75-7
Sequence: Gly-His-Lys (GHK) chelated with Cu²⁺
Structure Type: Naturally occurring copper-binding tripeptide complex
Pharmacological Classification
GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring **copper-binding tripeptide** found in human plasma, saliva, and urine. It exhibits potent regenerative and protective actions, influencing gene expression, promoting tissue remodeling, and modulating inflammation. GHK-Cu is widely studied for its applications in wound healing, skin regeneration, and anti-aging therapies.
Mechanism of Action
- Gene Expression Modulation: Alters the expression of numerous human genes, promoting regenerative processes and suppressing inflammation-related genes.
- Collagen and Glycosaminoglycan Synthesis: Stimulates the production of collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans, enhancing skin firmness and elasticity.
- Antioxidant Activity: Increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), reducing oxidative stress.
- Wound Healing: Accelerates wound healing by promoting angiogenesis and attracting immune cells to the site of injury.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
GHK-Cu does not interact with G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and thus does not involve **β-arrestin recruitment**. Its biological effects are mediated through direct modulation of gene expression and enzymatic activity rather than receptor binding.
Biological Effects
GHK-Cu has demonstrated multiple biological effects, including:
- Skin Regeneration: Enhances skin renewal, reduces fine lines and wrinkles, and improves skin tone.
- Hair Growth Promotion: Stimulates hair follicle activity, promoting hair growth and reducing hair loss.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines, aiding in the reduction of chronic inflammation.
- Neuroprotective Actions: Exhibits protective effects on nerve cells, potentially benefiting neurodegenerative conditions.
Molecular Targets and Pathways
| Target/Pathway | Effect of GHK-Cu |
|---|---|
| TGF-β1 | Downregulated, reducing fibrosis and scarring |
| MMPs | Regulates matrix metalloproteinases, balancing extracellular matrix remodeling |
| SOD | Enhances superoxide dismutase activity, combating oxidative stress |
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Half-Life: Approximately 30 minutes in plasma; rapid systemic clearance
- Bioavailability: Effective via topical application; systemic bioavailability is limited due to rapid degradation
- Metabolism: Metabolized by proteolytic enzymes; copper is released and utilized in various enzymatic processes
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized powder or aqueous solution
- Solubility: Soluble in water and aqueous buffers; stability enhanced at pH 5.0–7.0
- Storage: Store lyophilized powder at –20°C; reconstituted solutions should be stored at 4°C and used within 2–3 weeks
- Handling: Protect from light and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain stability
References
- Pickart L, Margolina A. GHK and DNA: Resetting the Human Genome to Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:151479. doi:10.1155/2014/151479.
- Pickart L, Margolina A. Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide in the Light of the New Gene Data. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1987. doi:10.3390/ijms19071987.
- Pickart L. The Human Tripeptide GHK and Tissue Remodeling. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2008;19(8):969–988. doi:10.1163/156856208784909345.
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero J, Margolina A. The Human Tripeptide GHK-Cu in Prevention of Oxidative Stress and Degenerative Conditions of Aging: Implications for Cognitive Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:324832. doi:10.1155/2012/324832.