Epitalon – Synthetic Tetrapeptide Telomerase Modulator
Chemical Identity
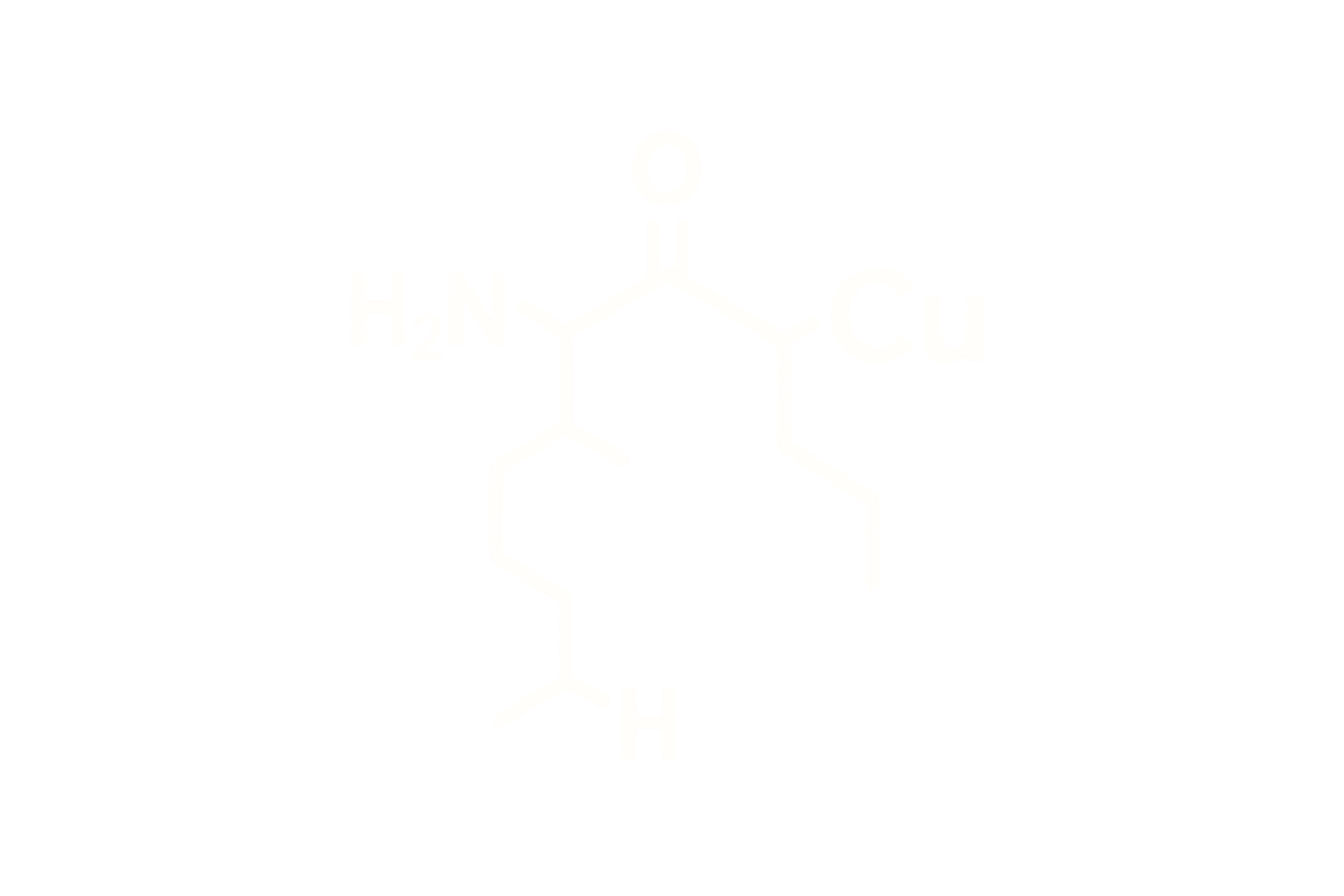
Chemical Name: Epitalon Acetate
Synonym: Epithalamin; Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Molecular Formula: C₁₄H₂₂N₄O₉
Molecular Weight: ~390.35 Da
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Structure Type: Synthetic tetrapeptide based on epithalamin, a natural extract of the pineal gland
Pharmacological Classification
Epitalon is a **synthetic peptide analog** of epithalamin, the naturally occurring peptide complex secreted by the pineal gland. It has been shown to **activate telomerase**, enhance chromatin stability, and promote longevity-related gene expression. It functions as a geroprotective regulator and is studied for its effects on aging, circadian rhythms, and cellular senescence.
Mechanism of Action
- Telomerase Activation: Promotes transcription of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) gene, preserving telomere length in somatic cells.
- Epigenetic Modulation: Enhances chromatin condensation and heterochromatin stability via DNA methylation remodeling.
- Neuroendocrine Regulation: Interacts with hypothalamic-pituitary axis and melatonin secretion, contributing to circadian rhythm stabilization.
- Antioxidant Gene Induction: Upregulates SOD2, catalase, and NRF2-regulated genes in oxidative stress models.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Epitalon is a **non-receptor-mediated peptide** and does not engage GPCR signaling pathways. There is no associated β-arrestin recruitment. Its bioactivity occurs via direct nuclear action, redox regulation, and chromatin interaction.
Biological Effects
Demonstrated effects include increased telomere length in fibroblasts, improved mitochondrial function, delayed onset of age-related diseases in rodent models, and life-span extension. Additional research has shown immunomodulatory and oncostatic (anti-tumor progression) properties in aged animals.
Cellular & Molecular Pathways
| Target | Effect of Epitalon |
|---|---|
| Telomerase (TERT) | Transcriptional activation |
| Melatonin Secretion | Normalized in pineal-deficient models |
| NF-κB / Inflammation | Inhibited expression in aged cells |
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Half-Life: Rapid tissue penetration; ~30–60 minutes systemic half-life
- Bioactivity Window: Sustained genomic modulation up to 48–72 hours post-exposure
- Metabolism: Renal clearance and enzymatic degradation
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, DMSO, dilute acid buffers
- Storage: –20°C; light- and moisture-protected
- Reconstitution: pH 5.0–6.0 recommended; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
References
- Khavinson VK, et al. Biogerontology. 2003;4(3):91–93.
- Khavinson V, et al. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006;27(6):857–862.
- Stambolsky P, et al. Aging (Albany NY). 2010;2(10):661–673.
- Anisimov VN, et al. Exp Gerontol. 2003;38(9):1043–1049.