Cagrilintide – Amylin Receptor Agonist
Chemical Identity
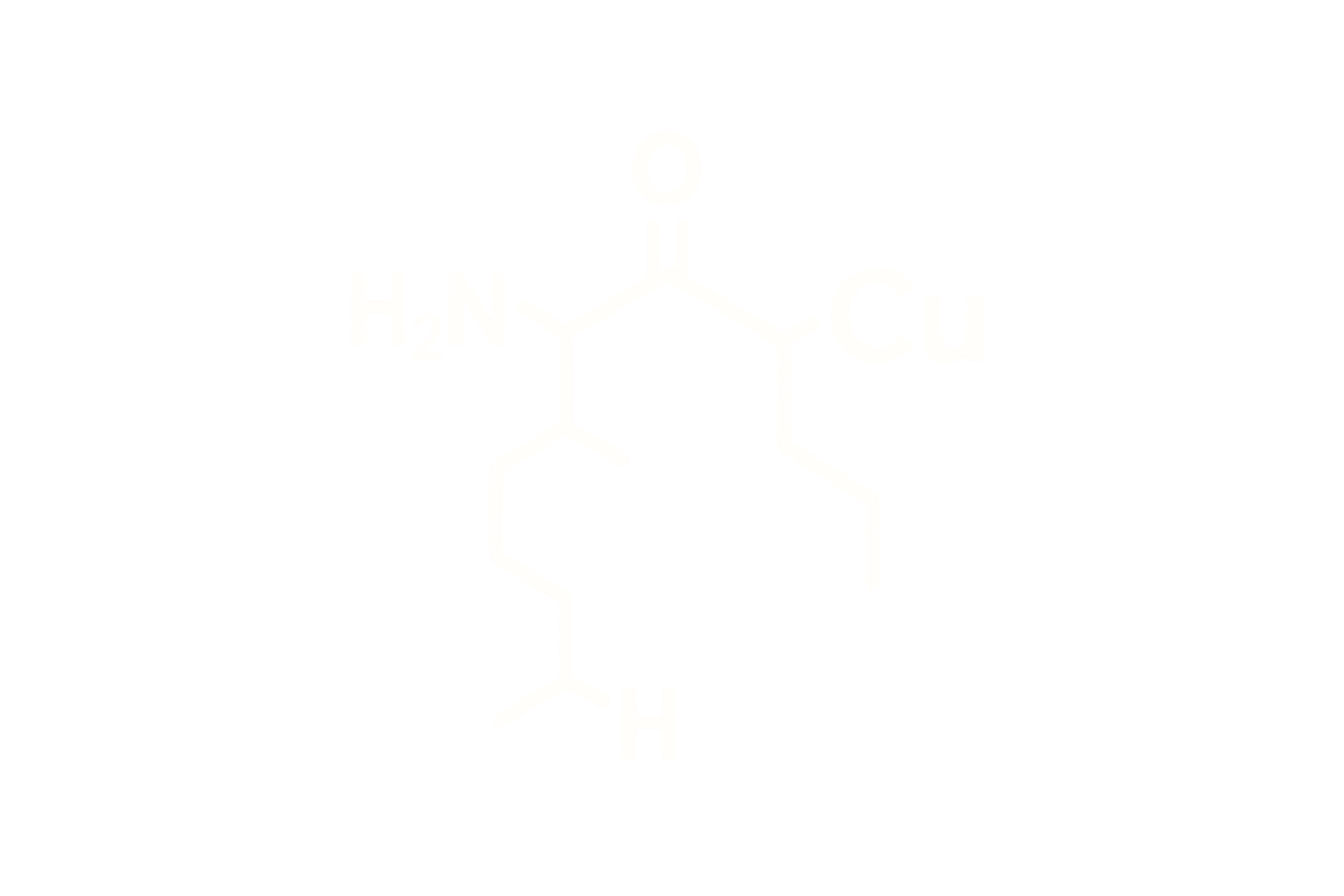
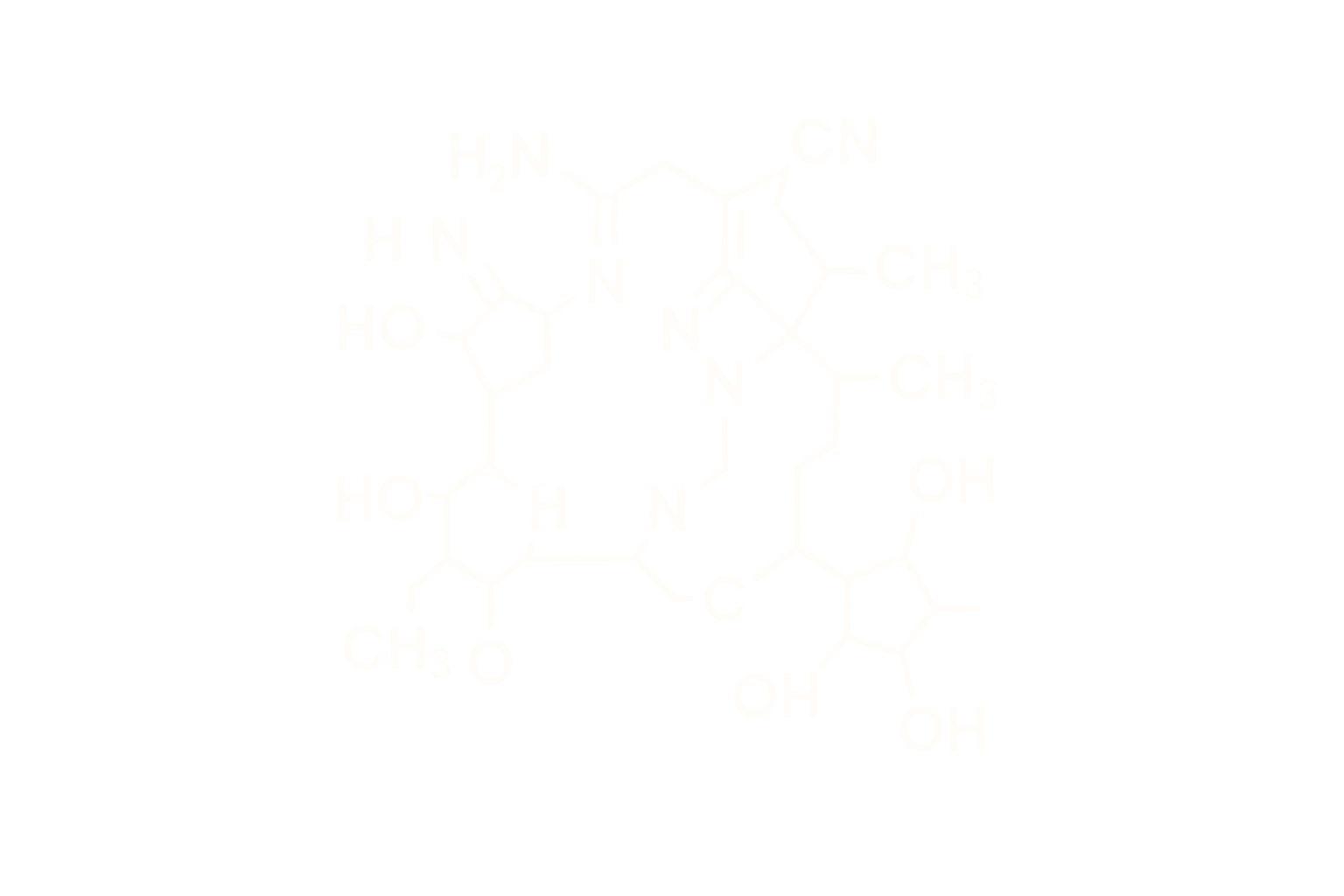
Chemical Name: Cagrilintide Acetate
Molecular Formula: C₁₉₄H₃₁₂N₅₄O₅₉S₂·C₂H₄O₂
Molecular Weight: ~4409 g/mol
CAS Number: 1415456-99-3
Sequence (Linear): Analog of human amylin with strategic amino acid substitutions to improve stability and receptor affinity
Modifications: Lipidation at lysine with fatty acid for albumin binding and extended half-life
Structure Type: Synthetic 37-amino acid linear peptide, lyophilized acetate salt
Pharmacological Classification
Cagrilintide is a long-acting **amylin receptor agonist (AMYR)** that acts on the **calcitonin receptor (CTR)** co-expressed with receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs), forming the AMY1/2/3 receptor subtypes. It is structurally related to human amylin and co-administered with GLP-1 receptor agonists for enhanced weight loss outcomes.
Mechanism of Action
- Amylin Receptor Activation: Engages AMY1–3 receptors in the area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarius to suppress appetite and modulate gastric emptying.
- Neurohormonal Effects: Enhances satiety signaling, reduces food reward, and complements GLP-1R agonism when used in combination therapy.
- Signaling: Primarily Gs-mediated cAMP production at CTR-RAMP complexes; downstream pathways regulate appetite and energy intake.
β-Arrestin Recruitment
Cagrilintide's β-arrestin recruitment has not been fully characterized at all amylin receptor subtypes, but current evidence suggests:
- CTR/AMY Receptors: Cagrilintide exhibits minimal β-arrestin recruitment compared to native amylin, favoring prolonged cAMP signaling and reduced receptor desensitization.
- This property supports sustained anorectic effects and lower tachyphylaxis risk over time.
Comparative β-Arrestin Profile
| Receptor | Native Ligand | β-Arrestin Recruitment | Cagrilintide Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMY1–3 (CTR + RAMPs) | Amylin | Moderate | Low (biased toward cAMP) |
References: Friedrichsen M et al., Nature Metabolism. 2021;3:1071–1080. Willard FS et al., Cell Reports. 2020;33(6):108293.
Molecular Engineering
Engineered to improve pharmacokinetics and receptor selectivity over native amylin. Fatty acid conjugation enhances albumin binding and prolongs half-life while substitutions improve stability against proteolysis and aggregation.
Pharmacokinetics (Non-Dosing)
- Elimination: Renal excretion of peptide fragments following enzymatic degradation
- Plasma Protein Binding: >98%, primarily to albumin
- Half-Life: ~7–8 days
Biological Effects
Reduces appetite and food intake via central mechanisms. Exhibits synergistic effects with GLP-1 receptor agonists on satiety and weight loss. No direct insulinotropic activity, distinguishing it mechanistically from GLP-1 analogs.
Preclinical Evidence
In rodent and primate models, cagrilintide induced sustained reductions in caloric intake, adiposity, and body weight. Combination with semaglutide resulted in additive effects on weight loss and metabolic markers.
Stability and Storage
- Form: Lyophilized acetate salt
- Solubility: Water, acidic buffer (pH 4–6), DMSO for analytical prep
- Storage: –20°C, moisture- and light-protected
- Reconstitution pH: 4.0–5.0 recommended
Comparative Mechanistic Summary
| Parameter | Amylin (native) | Cagrilintide |
|---|---|---|
| Receptor Targets | AMY1–3 | AMY1–3 |
| β-arrestin Recruitment | Moderate | Low |
| Half-Life | <1 hour | ~7–8 days |
| Albumin Binding | No | Yes |
References
- Friedrichsen M, et al. Nat Metab. 2021;3(8):1071–1080.
- Willard FS, et al. Cell Reports. 2020;33(6):108293.
- Madsen M, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(3):589–598.
- Andersen A, et al. Nature. 2023;621:148–155.